Install and Use COMET locally Through the Terminal

Some students may prefer to use the local version of jupyter that is accessible via browser, rather than through jupyter desktop. The latter allows for more customizability at the expense of a more intuitive installation and activation process.
1. Installing R
Before we install jupyter, we’ll need to install R and Rtools.
- Head to cran.r-project.org for windows and press
Download R-4.4.0 for Windows - Select
Okay > Nextand select your destination location. - Select the components
Main files,64-bit filesandMessage translations. Then, press next. - Select the toggle
No (acccept defaults)and press next. - Select both
save version number in registryandassociate R with .RData files. - Once the installation is complete, press
Finish.
- Head to cran.r-project.org for macOSx and select the release (on the left-hand side) suited for your device type.
- Open the installer and select
continue>continue>continue>agree>install.
2. Installing the R package Compiler
We’ll need to install a package compiler in order to compile R packages from source.
RTools is a program that allows us to compile R packages.
In the Rtools installer, press Next > Next (ensuring that both check boxes are ticked) > Install.
For Mac, you’ll need to install Xcode Command Line Tools instead.
- Open the Mac terminal. To do so, click on the spotlight icon in the menu bar and search for “terminal.”
- Install Homebrew: Homebrew is a package manager for MacOS which we will use to install Xcode. In the Mac terminal, paste:
/bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/HEAD/install.sh)"
This might prompt you to enter your user password, which is the password that you use to sign into your device (Note that for privacy reasons you won’t be able to see the characters that you type). Once you’ve entered your password, press enter. This may take a while to run.
- You should get an output similar to this:

Notice the warning. To fix this, we’ll need to add our installation to the system path. In the terminal, run:
(echo; echo 'eval "$(/opt/homebrew/bin/brew shellenv)"') >> ~/.zprofile
followed by:
eval "$(/opt/homebrew/bin/brew shellenv)"
which will add the required path to the installation.
- Verify installations: to check that Xtools is installed, run
$ brew doctorin the termial. This should display the output “Your system is ready to brew.”
3. Installing Conda and Jupyter
We can now install Jupyter. To do so, we’ll need to install minconda, a python environment manager, in order to create an envrionment in which we will use our required packages and activate Jupyter.
- Head to anaconda.com and select the installer that meets your computer requirements.
Ensure that, during the installation process, you select the following options:
- Add Miniconda3 to my PATH environment variable
- Register Miniconda3 as my default Python 3.12
Once installed, search for
Anaconda Prompt (miniconda3)in your files and open it as an administrator. This should open up a terminal.In the terminal, enter the following line code:
conda create -n comet jupyterlab r-essentials git r-tidyverse r-car r-stargazer r-estimatr
The first part of this command will create a new python environment called “comet”. An envrionment is an isolated space on your computer where you can work on a given project without the risk of breaking other projects. Essentially, this acts as a safety layer to protect our computer.
The second part of this command will add the required r packages for the COMET modules to the environment.
Lastly, to enable the environment, run conda activate comet_env.
4. Installing the R kernel
We’ll need to install the R kernel in order to use the R programming language in Jupyter. To do so, in the miniconda terminal, run r. This should result in the following output:
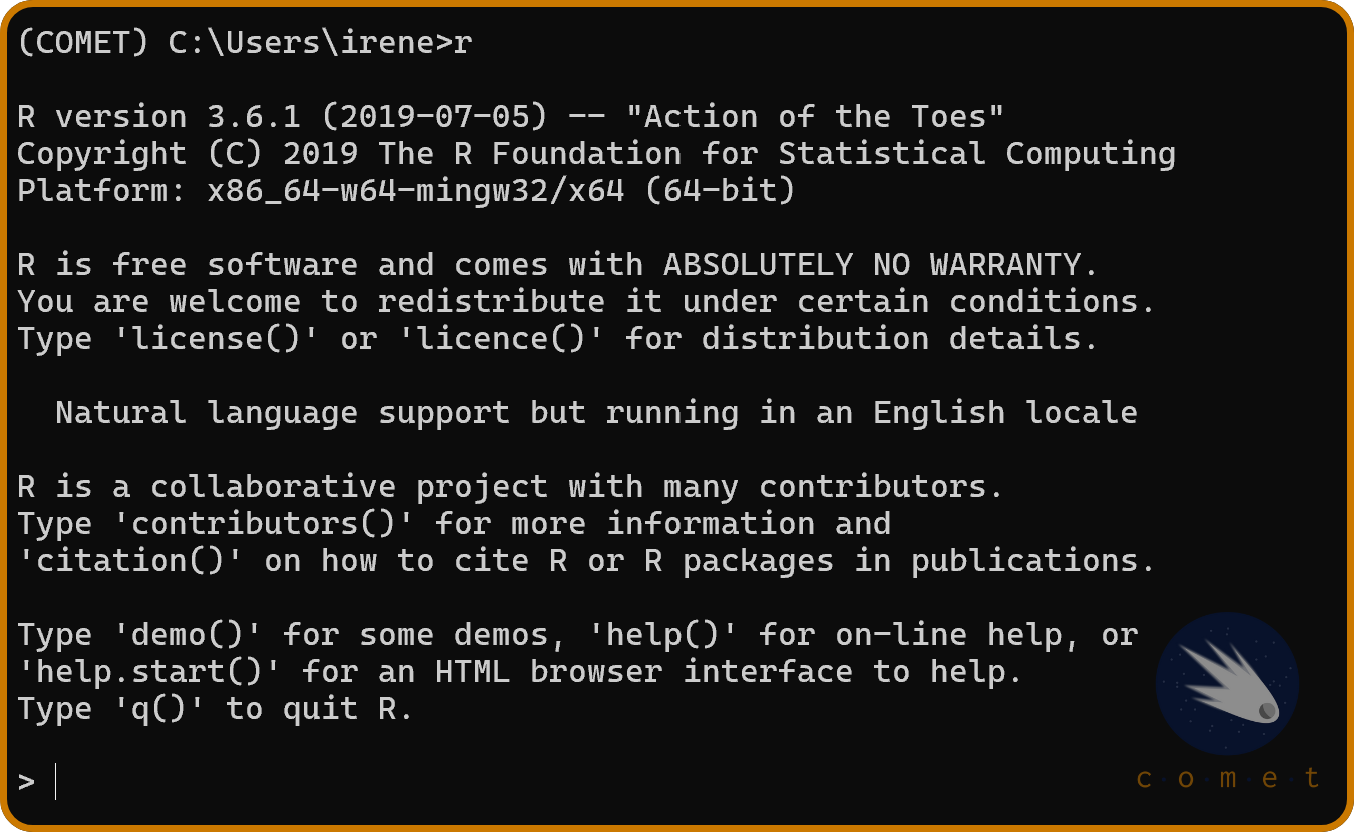
If you recieved this output, it means that everything has been set up correctly. Lastly, run the following lines of code in the terminal:
install.packages('IRkernel')
IRkernel::installspec()
This will prompt you to select a CRAN mirror. Select the one closest to you (if you are at UBC, this would be “Canada (MB)”.)
5. Opening Jupyter
Finally, to open Jupyter, open a new miniconda terminal. In the terminal, run the following command: jupyter lab. This will open up jupyter as a local copy on your search engine.
This terminal acts as your local Jupyter server. Closing it will shut down your server!
6. Opening the COMET modules
Lastly, you’ll want to download the COMET files. In the COMET website, press launch COMET from the top navigation bar, and then click on “launch locally”. This will download a file (main.zip) to you computer. Extract the .zip file to a folder on your computer that you can find easily and rename it from main to comet-project. Within jupyter, find this directory, and open it.